HAProxy: Balanceador de carga
- Clonamos el repositorio con el escenario.
git clone https://github.com/josedom24/vagrant_ansible_haproxy.git
- Una vez hagamos el
vagrant up entramos en cada una de las máquinas para ver las direcciones ip que les ha dado vagrant, entonces entramos en ansible/hosts y añadimos estas direcciones.
[servidor_ha]
frontend ansible_ssh_host=192.168.121.30 ansible_ssh_user=vagrant ansible_ssh_private_key_file=../.vagrant/machines/frontend/libvirt/private_key ansible_python_interpreter=/usr/bin/python3
[servidores_web]
backend1 ansible_ssh_host=192.168.121.250 ansible_ssh_user=vagrant ansible_ssh_private_key_file=../.vagrant/machines/backend1/libvirt/private_key ansible_python_interpreter=/usr/bin/python3
backend2 ansible_ssh_host=192.168.121.14 ansible_ssh_user=vagrant ansible_ssh_private_key_file=../.vagrant/machines/backend2/libvirt/private_key ansible_python_interpreter=/usr/bin/python3
- Pasamos la receta de ansible por el escenario.
alejandrogv@AlejandroGV:~/vagrant/servicios/vagrant_ansible_haproxy/ansible$ ansible-playbook site.yaml
PLAY [all] **********************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] **********************************************************************************
ok: [backend1]
ok: [backend2]
ok: [frontend]
TASK [commons : Ensure system is updated] ***************************************************************
changed: [backend2]
changed: [backend1]
changed: [frontend]
PLAY [servidor_ha] **************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] **********************************************************************************
ok: [frontend]
TASK [haproxy : install haproxy] ************************************************************************
changed: [frontend]
PLAY [servidores_web] ***********************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] **********************************************************************************
ok: [backend1]
ok: [backend2]
TASK [nginx : install nginx, php-fpm] *******************************************************************
changed: [backend1]
changed: [backend2]
TASK [nginx : Copy info.php] ****************************************************************************
changed: [backend2]
changed: [backend1]
TASK [nginx : Copy virtualhost default] *****************************************************************
changed: [backend2]
changed: [backend1]
RUNNING HANDLER [nginx : restart nginx] *****************************************************************
changed: [backend1]
changed: [backend2]
PLAY [servidores_web] ***********************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] **********************************************************************************
ok: [backend1]
ok: [backend2]
TASK [mariadb : ensure mariadb is installed] ************************************************************
changed: [backend2]
changed: [backend1]
TASK [mariadb : ensure mariadb binds to internal interface] *********************************************
changed: [backend2]
changed: [backend1]
RUNNING HANDLER [mariadb : restart mariadb] *************************************************************
changed: [backend2]
changed: [backend1]
PLAY [servidores_web] ***********************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] **********************************************************************************
ok: [backend2]
ok: [backend1]
TASK [wordpress : install unzip] ************************************************************************
changed: [backend2]
changed: [backend1]
TASK [wordpress : download wordpress] *******************************************************************
changed: [backend2]
changed: [backend1]
TASK [wordpress : unzip wordpress] **********************************************************************
changed: [backend2]
changed: [backend1]
TASK [wordpress : Copy wordpress.sql] *******************************************************************
changed: [backend2]
changed: [backend1]
TASK [wordpress : create database wordpress] ************************************************************
changed: [backend2]
changed: [backend1]
TASK [wordpress : create user mysql wordpress] **********************************************************
changed: [backend1] => (item=localhost)
changed: [backend2] => (item=localhost)
TASK [wordpress : copy wp-config.php] *******************************************************************
changed: [backend2]
changed: [backend1]
RUNNING HANDLER [wordpress : restart nginx] *************************************************************
changed: [backend2]
changed: [backend1]
PLAY RECAP **********************************************************************************************
backend1 : ok=20 changed=16 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
backend2 : ok=20 changed=16 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
frontend : ok=4 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
- Una vez terminado el escenario vamos a configurar la resolución estática, para ello primero debemos configurar el servicio de
haproxy en la máquina de frontend, así que añadimos el siguiente contenido en el fichero /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
frontend servidores_web
bind *:80
mode http
stats enable
stats uri /ha_stats
stats auth cda:cda
default_backend servidores_web_backend
backend servidores_web_backend
mode http
balance roundrobin
server backend1 10.0.0.10:80 check
server backend2 10.0.0.11:80 check
- Añadimos la dirección del frontend a nuestro fichero hosts de la maquina anfitriona.
192.168.121.30 www.example.org
- Comprobamos que funciona correctamente.
- Vamos a calcular el rendimiento con el balanceo de carga a dos nodos. Para ello haz varias pruebas y quedate con la media de peticiones/segundo. el primer paso para esto es instalar apache-utils.
vagrant@frontend:~$ sudo apt install apache2-utils
- Vamos a calcular el rendimiento tal como se nos indica.
alejandrogv@AlejandroGV:~$ ab -t 10 -c 100 -k http://www.example.org/wordpress/
This is ApacheBench, Version 2.3 <$Revision: 1879490 $>
Copyright 1996 Adam Twiss, Zeus Technology Ltd, http://www.zeustech.net/
Licensed to The Apache Software Foundation, http://www.apache.org/
Benchmarking www.example.org (be patient)
Finished 799 requests
Server Software: nginx/1.18.0
Server Hostname: www.example.org
Server Port: 80
Document Path: /wordpress/
Document Length: 27248 bytes
Concurrency Level: 100
Time taken for tests: 10.004 seconds
Complete requests: 799
Failed requests: 0
Keep-Alive requests: 0
Total transferred: 22002713 bytes
HTML transferred: 21819857 bytes
Requests per second: 79.87 [#/sec] (mean)
Time per request: 1252.029 [ms] (mean)
Time per request: 12.520 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests)
Transfer rate: 2147.90 [Kbytes/sec] received
Connection Times (ms)
min mean[+/-sd] median max
Connect: 0 0 0.5 0 2
Processing: 43 1174 263.7 1183 1511
Waiting: 16 1141 259.2 1151 1465
Total: 43 1175 263.2 1183 1512
Percentage of the requests served within a certain time (ms)
50% 1183
66% 1210
75% 1344
80% 1387
90% 1438
95% 1460
98% 1474
99% 1483
100% 1512 (longest request)
- Vamos a volver a hacer y comprobar que baja el numero de respuestas (Lo he vuelto a hacer varias veces y no baja significativamente).
Requests per second: 75.60 [#/sec] (mean)
- Ahora vamos a apagar uno de los nodos usando
hatop, paquete que debemos instalar.
hatop -s /run/haproxy/admin.sock
- Usando este comando nos aparecerá esta pantalla, si nos situamos encima de uno de los nodos y pulsamos
F10 se desactivará.
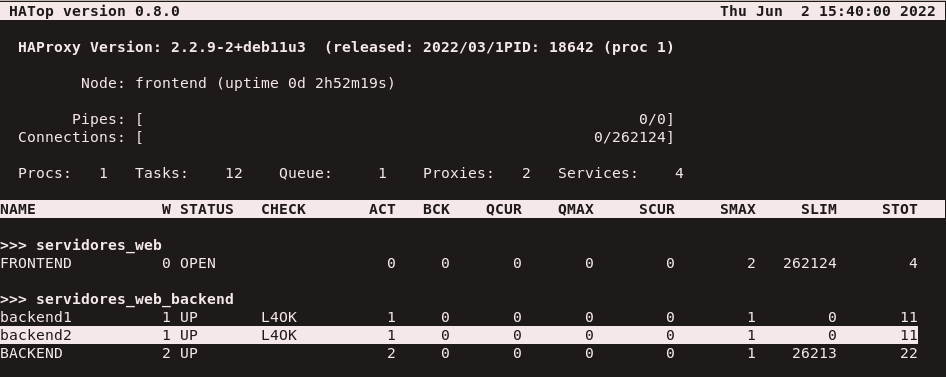
- Comprobamos el numero de respuestas, el cual podemos comprobar que ha bajado significativamente.
Requests per second: 53.18 [#/sec] (mean)
- Hemos vuelto a activar el nodo pulsado
F9, Ahora instalaremos un nuevo nodo al que pasaremos la receta de ansible y lo configuramos en el haproxy.
server backend3 192.168.121.220:80 check
- Reiniciamos el servicio y comprobamos el balanceo nuevamente.
Requests per second: 101.75 [#/sec] (mean)
Memcached
- Tenemos un nuevo escenario al que como el anterior hemos pasado una receta de ansible y también tiene instalado un wordpress. En este escenario solo tenemos una maquina y el primer paso en ella será instalar el paquete
memcached.
vagrant@servidorweb:~$ sudo apt install php-memcached memcached
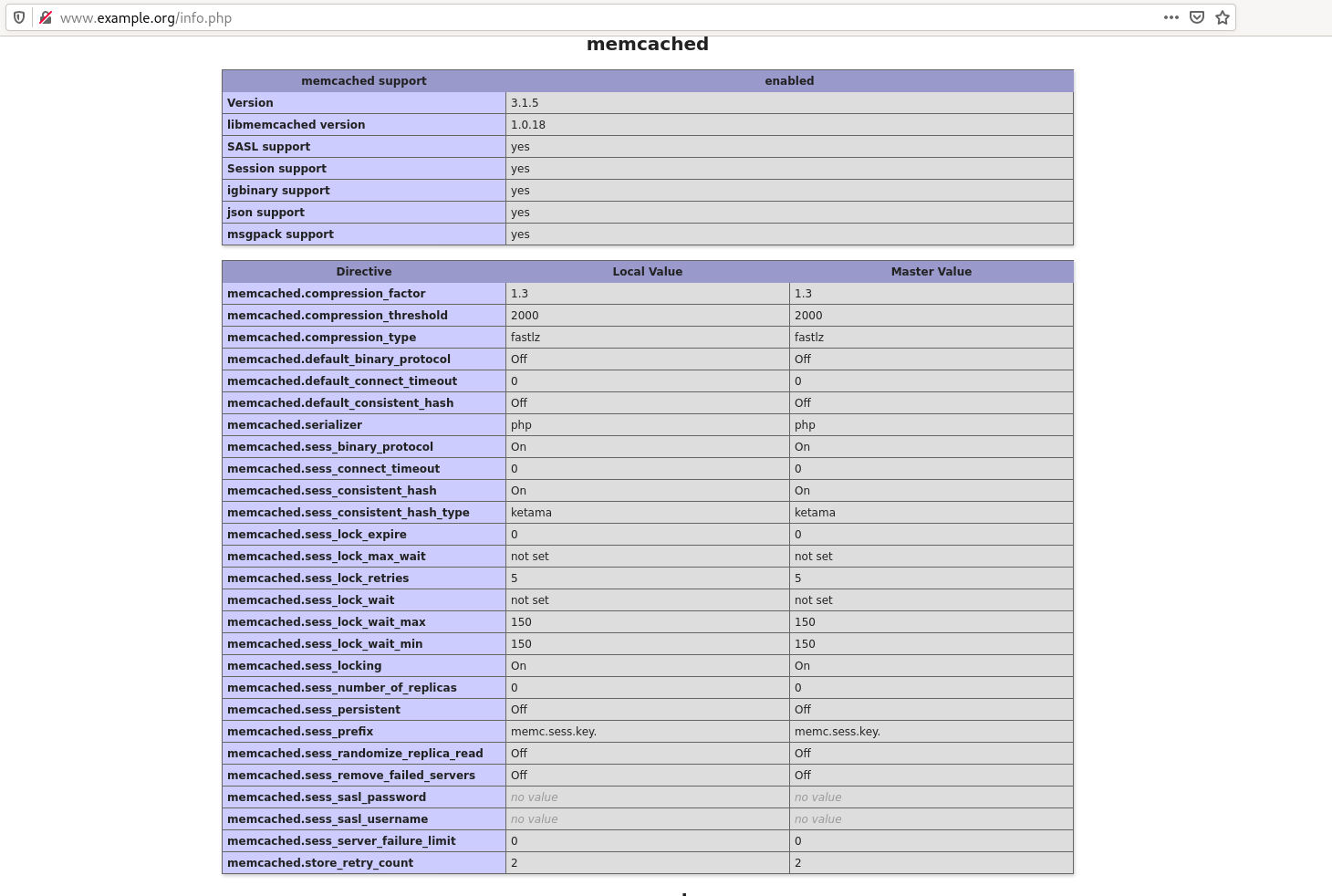
- Añadimos a nuestro
etc/hosts la nueva dirección y accedemos a la página, concretamente el info.php y si bajamos comprobaremos que tenemos instalado este paquete.
- Vamos a instalar en wordpress un plugin que nos permite trabajar con memecached. para ello nos dirigimos a la zona de administración, entramos en plugins e instalamos
WP-FFPC.
- Después de instalarlo nos aparecerá un botón de activar que pulsaremos y seguidamente tendremos una serie de mensajes de error que iremos solucionando.
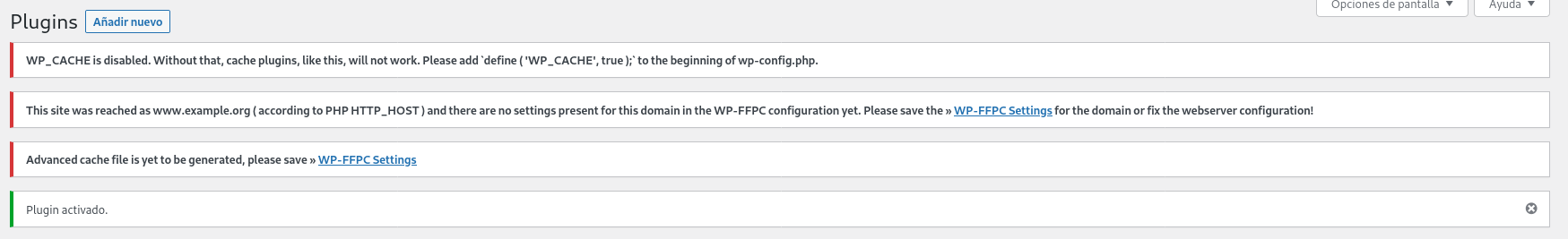
- En primer lugar nos dirigimos al fichero
/var/www/html/wordpress/wp-config.php y añadimos la siguiente línea:
define('WP_CACHE', true);
- Y nos vamos a los settings del plugin, donde podremos cambiar algunos parametros, aunque no cambiemos ninguno guardamos los cambios y así se configurará.
- Ahora vamos a hacer pruebas de rendimiento y comprobar si ha aumentado.
alejandrogv@AlejandroGV:~$ ab -t 10 -c 100 -k http://www.example.org/wordpress/
This is ApacheBench, Version 2.3 <$Revision: 1879490 $>
Copyright 1996 Adam Twiss, Zeus Technology Ltd, http://www.zeustech.net/
Licensed to The Apache Software Foundation, http://www.apache.org/
Benchmarking www.example.org (be patient)
Completed 5000 requests
Completed 10000 requests
Finished 10740 requests
Server Software: nginx/1.18.0
Server Hostname: www.example.org
Server Port: 80
Document Path: /wordpress/
Document Length: 27215 bytes
Concurrency Level: 100
Time taken for tests: 10.001 seconds
Complete requests: 10740
Failed requests: 0
Keep-Alive requests: 0
Total transferred: 294673386 bytes
HTML transferred: 292289100 bytes
Requests per second: 1073.93 [#/sec] (mean)
Time per request: 93.116 [ms] (mean)
Time per request: 0.931 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests)
Transfer rate: 28774.89 [Kbytes/sec] received
Connection Times (ms)
min mean[+/-sd] median max
Connect: 0 0 0.3 0 6
Processing: 4 89 7.1 88 369
Waiting: 3 89 7.1 88 361
Total: 9 89 6.9 88 369
Percentage of the requests served within a certain time (ms)
50% 88
66% 89
75% 90
80% 90
90% 96
95% 102
98% 105
99% 106
100% 369 (longest request)
- Vemos que con la primera prueba ya ha mejorado bastante el rendimiento, llegando a las 1073 respuestas. Lo hemos hecho varias veces más y vemos que el rendimiento sube un poco.
Requests per second: 1127.43 [#/sec] (mean)
Varnish
- Usaremos este mismo escenario y configuraremos varnish, por supuesto primero debemos instalarlo.
vagrant@servidorweb:~$ sudo apt install varnish
- Este servicio escuchará por el puerto 80, así que debemos configurar nginx para que escuche por otro puerto en el fichero
/etc/nginx/sites-available/default.
server {
listen 8080 default_server;
listen [::]:8080 default_server;
- Configuramos varnish para que use este puerto en el fichero
/etc/default/varnish
DAEMON_OPTS="-a :80 \
-T localhost:6082 \
-f /etc/varnish/default.vcl \
-S /etc/varnish/secret \
-s malloc,256m"
- Y redirigirlas al 8080 donde escucha nginx, esto lo haremos el fichero
/etc/varnish/default.vcl.
backend default {
.host = "127.0.0.1";
.port = "8080";
}
- También debemos configurar la unidad de systemd
/lib/systemd/system/varnish.service.
ExecStart=/usr/sbin/varnishd \
-j unix,user=vcache \
-F \
-a :80 \
-T localhost:6082 \
-f /etc/varnish/default.vcl \
-S /etc/varnish/secret \
-s malloc,256m
- Después de reiniciar el demonio vamos a comprobar que varnish a cogido la configuración.
● varnish.service - Varnish Cache, a high-performance HTTP accelerator
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/varnish.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Fri 2022-06-03 12:17:56 UTC; 53s ago
Docs: https://www.varnish-cache.org/docs/
man:varnishd
Main PID: 26157 (varnishd)
Tasks: 217 (limit: 528)
Memory: 112.3M
CPU: 251ms
CGroup: /system.slice/varnish.service
├─26157 /usr/sbin/varnishd -j unix,user=vcache -F -a :80 -T localhost:6082 -f /etc/varnish/default.vcl -S /etc/varnish/secret -s malloc,256m
└─26169 /usr/sbin/varnishd -j unix,user=vcache -F -a :80 -T localhost:6082 -f /etc/varnish/default.vcl -S /etc/varnish/secret -s malloc,256m
- Una vez instalado y configurado vamos a realizar las pruebas de rendimiento.
alejandrogv@AlejandroGV:~$ ab -t 10 -c 100 -k http://www.example.org/wordpress/
This is ApacheBench, Version 2.3 <$Revision: 1879490 $>
Copyright 1996 Adam Twiss, Zeus Technology Ltd, http://www.zeustech.net/
Licensed to The Apache Software Foundation, http://www.apache.org/
Benchmarking www.example.org (be patient)
Completed 5000 requests
Completed 10000 requests
Completed 15000 requests
Completed 20000 requests
Completed 25000 requests
Completed 30000 requests
Finished 34518 requests
Server Software: nginx/1.18.0
Server Hostname: www.example.org
Server Port: 80
Document Path: /wordpress/
Document Length: 7860 bytes
Concurrency Level: 100
Time taken for tests: 10.000 seconds
Complete requests: 34518
Failed requests: 34517
(Connect: 0, Receive: 0, Length: 34517, Exceptions: 0)
Non-2xx responses: 1
Keep-Alive requests: 34517
Total transferred: 951896908 bytes
HTML transferred: 939372069 bytes
Requests per second: 3451.77 [#/sec] (mean)
Time per request: 28.971 [ms] (mean)
Time per request: 0.290 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests)
Transfer rate: 92957.99 [Kbytes/sec] received
Connection Times (ms)
min mean[+/-sd] median max
Connect: 0 0 0.2 0 5
Processing: 0 19 19.8 17 3545
Waiting: 0 19 19.8 17 3540
Total: 0 19 19.8 17 3545
Percentage of the requests served within a certain time (ms)
50% 17
66% 19
75% 20
80% 21
90% 23
95% 27
98% 33
99% 38
100% 3545 (longest request)
- Vemos que en la primera ya ha subido considerablemente a 3451, vamos a hacer algunas más y a comprobar la última que hagamos:
Requests per second: 5978.24 [#/sec] (mean)
- Vamos a comprobar el
acces.log para ver cuantas peticiones han llegado al servidor.
127.0.0.1 - - [03/Jun/2022:12:22:21 +0000] "GET /wordpress/ HTTP/1.1" 200 6701 "-" "ApacheBench/2.3"
127.0.0.1 - - [03/Jun/2022:12:27:46 +0000] "GET /wordpress/ HTTP/1.1" 200 6701 "-" "ApacheBench/2.3"
- Solo hay dos registros con 5 minutos de diferencia, esto debido a la duración de la cache.





